This is a step-by-step guide on setting up OpenFaaS on GKE with the following characteristics:
- two OpenFaaS instances, one for staging and one for production use, isolated with network policies
- a dedicated node pool for OpenFaaS long-running services
- a dedicated node pool of preemptible VMs for OpenFaaS functions
- autoscaling for functions and their underling infrastructure
- secure OpenFaaS ingress with Let’s Encrypt TLS and authentication
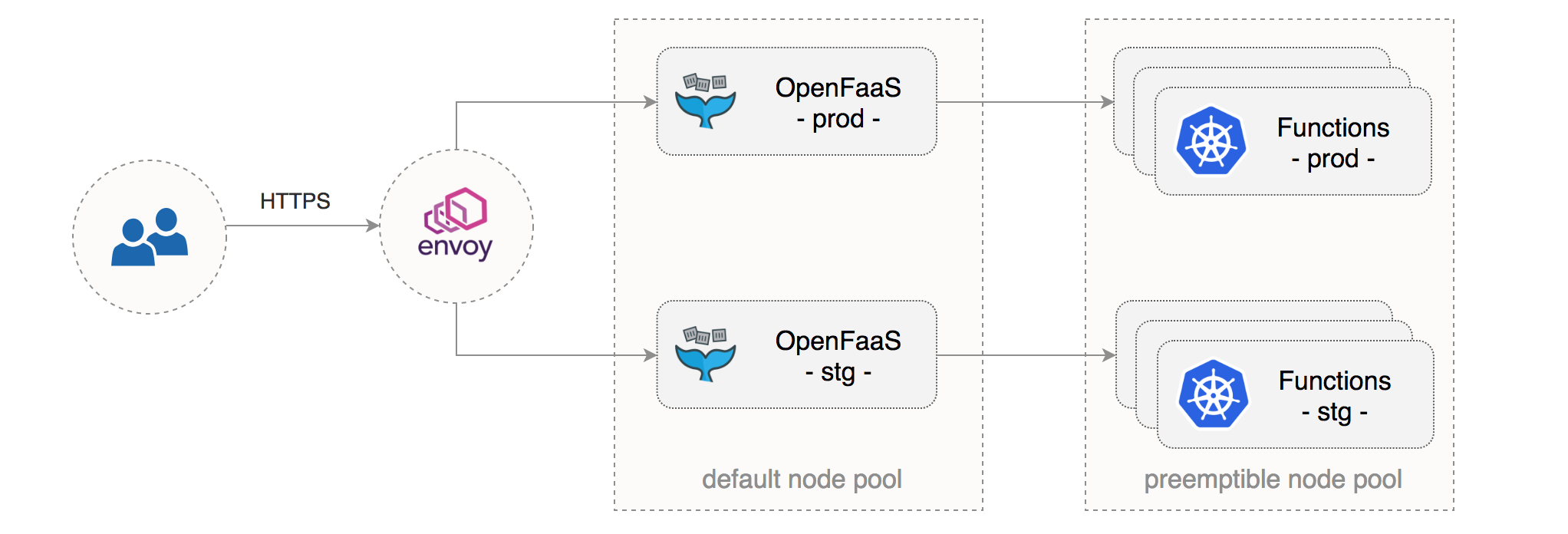
This setup can enable multiple teams to share the same CD pipeline with staging/production environments hosted on GKE and development taking place on a local environment such as Minikube or Docker for Mac.
GKE cluster setup
Create a cluster with two nodes and network policy enabled:
k8s_version=$(gcloud container get-server-config --format=json | jq -r '.validNodeVersions[0]')
gcloud container clusters create openfaas \
--cluster-version=${k8s_version} \
--zone=europe-west3-a \
--num-nodes=2 \
--machine-type=n1-standard-1 \
--no-enable-cloud-logging \
--disk-size=30 \
--enable-autorepair \
--enable-network-policy \
--scopes=gke-default,compute-rw,storage-rw
The above command will create a node pool named default-pool made of n1-standard-1 (vCPU: 1, RAM 3.75GB, DISK: 30GB) VMs.
You will use the default pool to run the following OpenFaaS components:
- Core services (Gateway and Kubernetes Operator)
- Async services (NATS streaming and queue worker)
- Monitoring and autoscaling services (Prometheus and Alertmanager)
Create a node pool of n1-highcpu-4 (vCPU: 4, RAM 3.60GB, DISK: 30GB) preemptible VMs with autoscaling enabled:
gcloud container node-pools create fn-pool \
--cluster=openfaas \
--preemptible \
--node-version=${k8s_version} \
--zone=europe-west3-a \
--num-nodes=1 \
--enable-autoscaling --min-nodes=2 --max-nodes=4 \
--machine-type=n1-highcpu-4 \
--disk-size=30 \
--enable-autorepair \
--scopes=gke-default
Preemptible VMs are up to 80% cheaper than regular instances but will be terminated and replaced after a maximum of 24 hours. In order to avoid all nodes to be terminated at the same time, wait for 30 minutes and scale up the fn pool to two nodes:
gcloud container clusters resize openfaas \
--size=2 \
--node-pool=fn-pool \
--zone=europe-west3-a
When a VM is preempted it gets logged here:
gcloud compute operations list | grep compute.instances.preempted
The above setup along with a GCP load balancer forwarding rule and a 30GB ingress traffic will cost you $150 per month. The cost estimation was generated with the Google Cloud pricing calculator on 31 July 2018 and could change any time.
GKE addons setup
Set up credentials for kubectl:
gcloud container clusters get-credentials openfaas -z=europe-west3-a
Create a cluster admin user:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding "cluster-admin-$(whoami)" \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--user="$(gcloud config get-value core/account)"
Install Helm CLI with Homebrew:
brew install kubernetes-helm
Create a service account and a cluster role binding for Tiller:
kubectl -n kube-system create sa tiller
kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller-cluster-rule \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller
Deploy Tiller in the kube-system namespace:
helm init --service-account tiller
When exposing OpenFaaS on the internet you should enable HTTPS to encrypt all traffic. To do that you’ll need the following tools:
- Heptio Contour as Kubernetes Ingress controller (or another ingress controller such as Nginx)
- JetStack cert-manager as Let’s Encrypt provider
Heptio Contour is an ingress controller based on Envoy reverse proxy that supports dynamic configuration updates. Install Contour with:
kubectl apply -f https://j.hept.io/contour-deployment-rbac
Find the Contour address with:
kubectl -n heptio-contour describe svc/contour | grep Ingress | awk '{ print $NF }'
Go to your DNS provider and create an A record for each OpenFaaS instance:
$ host openfaas.example.com
openfaas.example.com has address 35.197.248.216
$ host openfaas-stg.example.com
openfaas-stg.example.com has address 35.197.248.217
Install cert-manager with Helm:
helm install --name cert-manager \
--namespace kube-system \
stable/cert-manager
Create a cluster issuer definition (replace email@example.com with a valid email address):
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt
spec:
acme:
email: email@example.com
http01: {}
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-cert
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
Save the above resource as letsencrypt-issuer.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./letsencrypt-issuer.yaml
Network policies setup
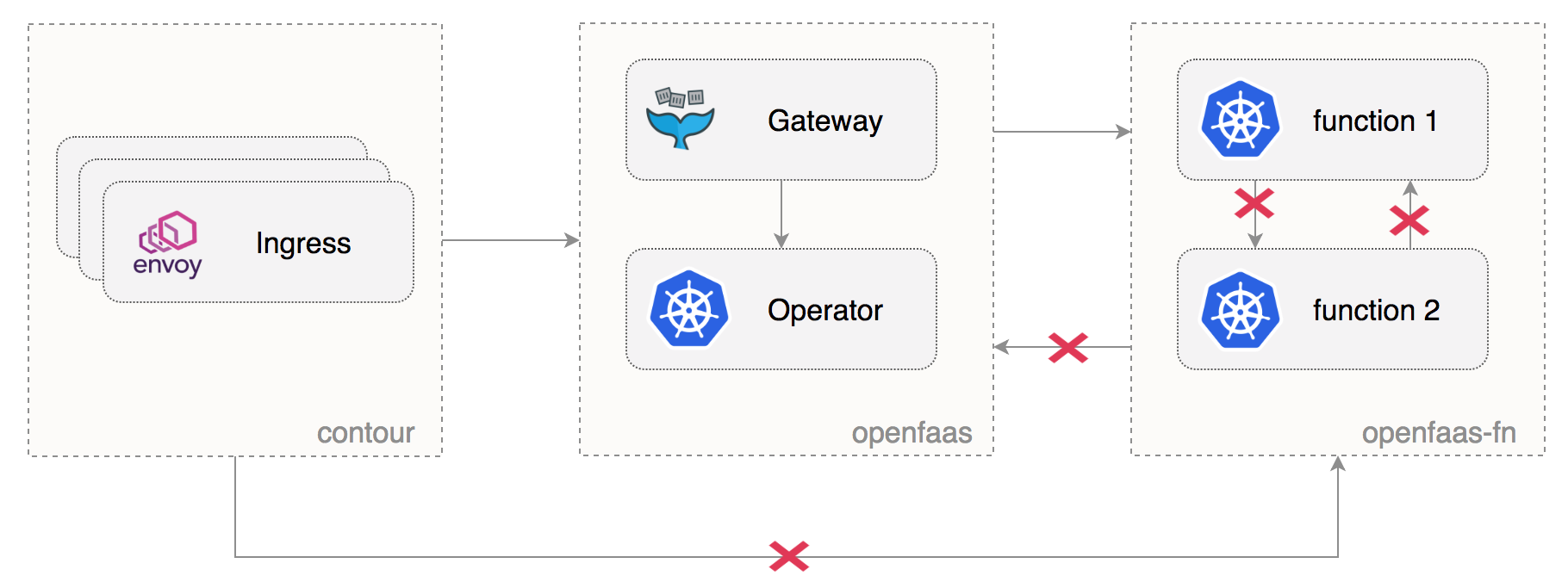
Create the OpenFaaS dev and prod namespaces:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: openfaas-stg
labels:
role: openfaas-system
access: openfaas-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: openfaas-stg-fn
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: openfaas-prod
labels:
role: openfaas-system
access: openfaas-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: openfaas-prod-fn
Save the above resource as openfaas-ns.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./openfaas-ns.yaml
Allow ingress traffic from the heptio-contour namespace to both OpenFaaS environments:
kubectl label namespace heptio-contour access=openfaas-system
Create network policies to isolate the OpenFaaS core services from the function namespaces:
kind: NetworkPolicy
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: openfaas-stg
namespace: openfaas-stg
spec:
policyTypes:
- Ingress
podSelector: {}
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
access: openfaas-system
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: openfaas-stg-fn
namespace: openfaas-stg-fn
spec:
policyTypes:
- Ingress
podSelector: {}
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
role: openfaas-system
---
kind: NetworkPolicy
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: openfaas-prod
namespace: openfaas-prod
spec:
policyTypes:
- Ingress
podSelector: {}
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
access: openfaas-system
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: openfaas-prod-fn
namespace: openfaas-prod-fn
spec:
policyTypes:
- Ingress
podSelector: {}
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
role: openfaas-system
Save the above resource as network-policies.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./network-policies.yaml
Note that the above configuration will prohibit functions from calling each other or from reaching the OpenFaaS core services.
OpenFaaS staging setup
Generate a random password and create an OpenFaaS credentials secret:
stg_password=$(head -c 12 /dev/urandom | shasum | cut -d' ' -f1)
kubectl -n openfaas-stg create secret generic basic-auth \
--from-literal=basic-auth-user=admin \
--from-literal=basic-auth-password=$stg_password
Create the staging configuration (replace example.com with your own domain):
functionNamespace: openfaas-stg-fn
basic_auth: true
exposeServices: false
operator:
create: true
createCRD: true
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "contour"
certmanager.k8s.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt"
contour.heptio.com/request-timeout: "30s"
contour.heptio.com/num-retries: "3"
contour.heptio.com/retry-on: "gateway-error"
hosts:
- host: openfaas-stg.example.com
serviceName: gateway
servicePort: 8080
path: /
tls:
- secretName: openfaas-cert
hosts:
- openfaas-stg.example.com
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: cloud.google.com/gke-preemptible
operator: DoesNotExist
Note that the OpenFaaS components will be running on the default pool due to the affinity constraint cloud.google.com/gke-nodepool=default-pool.
Save the above file as openfaas-stg.yaml and install OpenFaaS staging instance from the project helm repository:
helm repo add openfaas https://openfaas.github.io/faas-netes/
helm upgrade openfaas-stg --install openfaas/openfaas \
--namespace openfaas-stg \
-f openfaas-stg.yaml
In a couple of seconds cert-manager should fetch a certificate from LE:
kubectl -n kube-system logs deployment/cert-manager
Certificate issued successfully
OpenFaaS production setup
Generate a random password and create the basic-auth secret in the openfaas-prod namespace:
password=$(head -c 12 /dev/urandom | shasum | cut -d' ' -f1)
kubectl -n openfaas-prod create secret generic basic-auth \
--from-literal=basic-auth-user=admin \
--from-literal=basic-auth-password=$password
Create the production configuration (replace example.com with your own domain):
functionNamespace: openfaas-prod-fn
basic_auth: true
exposeServices: false
operator:
create: true
createCRD: false
gateway:
replicas: 2
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "contour"
certmanager.k8s.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt"
contour.heptio.com/request-timeout: "30s"
contour.heptio.com/num-retries: "3"
contour.heptio.com/retry-on: "gateway-error"
hosts:
- host: openfaas.example.com
serviceName: gateway
servicePort: 8080
path: /
tls:
- secretName: openfaas-cert
hosts:
- openfaas.example.com
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: cloud.google.com/gke-preemptible
operator: DoesNotExist
podAntiAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 100
podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: gateway
release: openfaas-prod
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
For production the OpenFaaS gateway is scaled to two replicas and with the pod anti-affinity rule we make sure that each replica will run on a different node.
Note that operator.createCRD is set to false since the functions.openfaas.com custom resource definition is already present on the cluster.
Save the above file as openfaas-prod.yaml and install OpenFaaS instance from the project helm repository:
helm upgrade openfaas-prod --install openfaas/openfaas \
--namespace openfaas-prod \
-f openfaas-prod.yaml
OpenFaaS functions operations
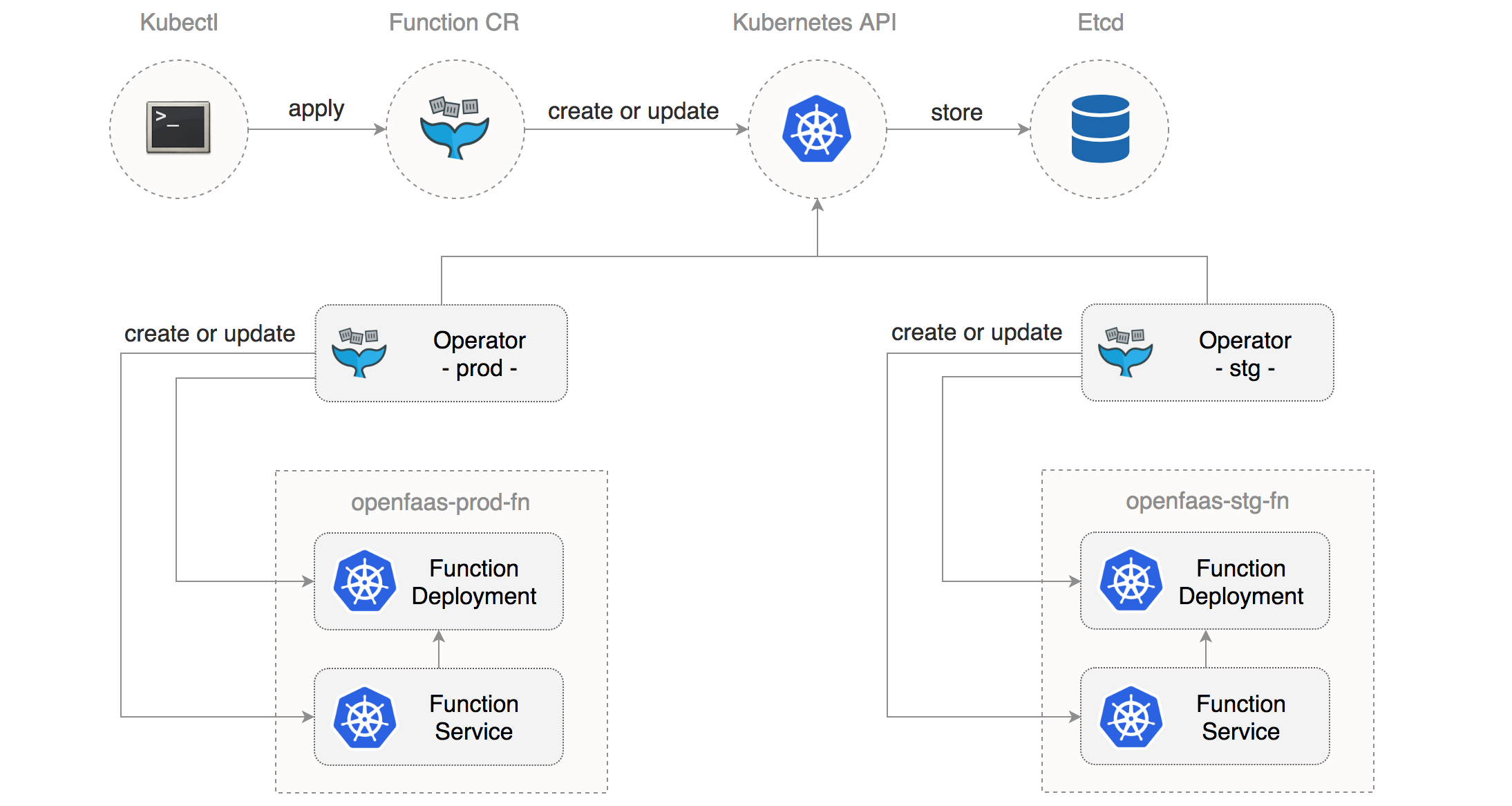
Using the OpenFaaS CRD you can define functions as Kubernetes custom resource:
apiVersion: openfaas.com/v1alpha2
kind: Function
metadata:
name: certinfo
spec:
name: certinfo
image: stefanprodan/certinfo:latest
labels:
com.openfaas.scale.min: "2"
com.openfaas.scale.max: "12"
com.openfaas.scale.factor: "4"
limits:
cpu: "1000m"
memory: "128Mi"
requests:
cpu: "10m"
memory: "64Mi"
constraints:
- "cloud.google.com/gke-preemptible=true"
Note that this function will be running on the fn pool due to the affinity constraint cloud.google.com/gke-preemptible=true.
Save the above resource as certinfo.yaml and use kubectl to deploy the function on both instances:
kubectl -n openfaas-stg-fn apply -f certinfo.yaml
kubectl -n openfaas-prod-fn apply -f certinfo.yaml
Verify both endpoints are live:
curl -d "openfaas-stg.example.com" https://openfaas-stg.example.com/function/certinfo
Issuer Let's Encrypt Authority X3
....
curl -d "openfaas.example.com" https://openfaas.example.com/function/certinfo
Issuer Let's Encrypt Authority X3
....
To manage functions on Kubernetes you can use kubectl but for development you’ll need the OpenFaaS CLI. You can install faas-cli and connect to the staging instance with:
curl -sL https://cli.openfaas.com | sudo sh
echo $stg_password | faas-cli login -u admin --password-stdin -g https://openfaas-stg.example.com
Using faas-cli and kubectl a development workflow would look like this:
- Create a function from a code template
faas-cli new myfn --lang go --prefix gcr.io/project-id - Implement the function handler
- Build the function as a Docker image
faas-cli build -f myfn.yaml - Run the function on your local cluster
faas-cli deploy -f myfn.yaml -g localhost:8080 - Push the image to GCP Container Registry
faas-cli push -f myfn.yml - Generate the function Kubernetes custom resource
faas-cli generate --yaml myfn.yaml > myfn-k8s.yaml - Deploy it on the staging environment
kubectl -n openfaas-stg-fn apply -f myfn-k8s.yaml - Run integration tests on staging
cat test.json | faas-cli invoke myfn -g https://openfaas-stg.exmaple.com - Promote the function to production
kubectl -n openfaas-prod-fn apply -f myfn-k8s.yaml
This guide was originally posted on OpenFaaS Blog https://www.openfaas.com/blog/gke-multi-stage/
