The OpenFaaS team recently released a Kubernetes operator for OpenFaaS. The OpenFaaS Operator can be run with OpenFaaS on any Kubernetes service, in this post I will show you step-by-step instructions on how to deploy to Amazon’s managed Kubernetes service (EKS).
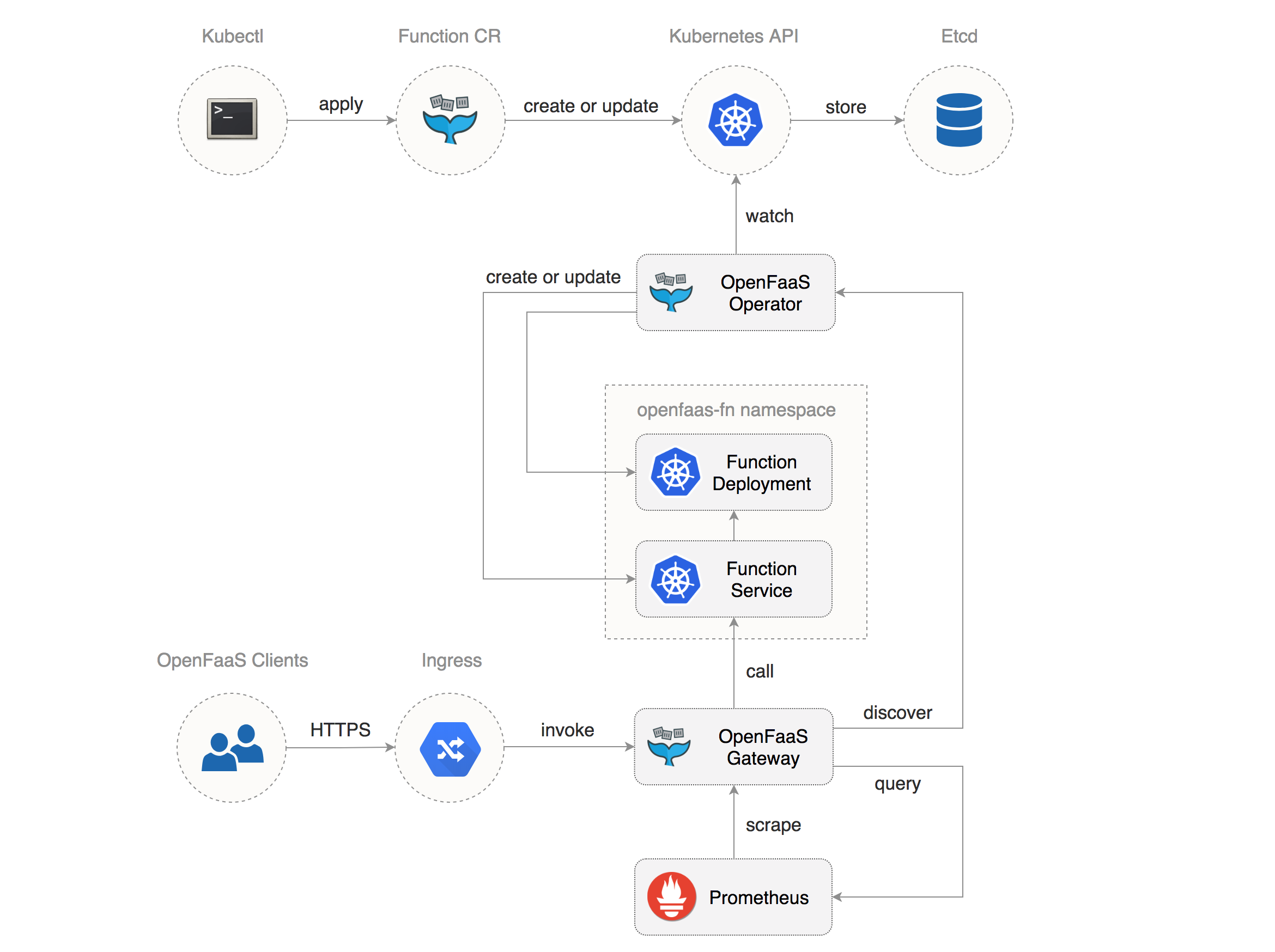
The OpenFaaS Operator comes with an extension to the Kubernetes API that allows you to manage OpenFaaS functions in a declarative manner. The operator implements a control loop that tries to match the desired state of your OpenFaaS functions, defined as a collection of custom resources, with the actual state of your cluster.
Setup a Kubernetes cluster with eksctl
In order to create an EKS cluster you can use eksctl. eksctl is an open source command-line utility made by Weaveworks in collaboration with Amazon, it’s written in Go and is based on EKS CloudFormation templates.
On MacOS you can install eksctl with Homebrew:
brew install weaveworks/tap/eksctl
Create an EKS cluster with:
eksctl create cluster --name=openfaas \
--nodes=2 \
--region=us-west-2 \
--node-type=m5.xlarge \
--auto-kubeconfig
eksctl offers many options when creating a cluster:
$ eksctl create cluster --help
Usage:
eksctl create cluster [flags]
Flags:
--auto-kubeconfig save kubconfig file by cluster name, e.g. "/Users/stefan/.kube/eksctl/clusters/extravagant-wardrobe-1531126688"
--aws-api-timeout duration number of seconds after which to timeout AWS API operations (default 20m0s)
--full-ecr-access enable full access to ECR
-h, --help help for cluster
--kubeconfig string path to write kubeconfig (incompatible with --auto-kubeconfig) (default "/Users/aleph/.kube/config")
-n, --name string EKS cluster name (generated if unspecified, e.g. "extravagant-wardrobe-1531126688")
-t, --node-type string node instance type (default "m5.large")
-N, --nodes int total number of nodes (for a static ASG) (default 2)
-M, --nodes-max int maximum nodes in ASG
-m, --nodes-min int minimum nodes in ASG
-p, --profile string AWS creditials profile to use (overrides the AWS_PROFILE environment variable)
-r, --region string AWS region (default "us-west-2")
--set-kubeconfig-context if true then current-context will be set in kubeconfig; if a context is already set then it will be overwritten (default true)
--ssh-public-key string SSH public key to use for nodes (import from local path, or use existing EC2 key pair) (default "~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub")
--write-kubeconfig toggle writing of kubeconfig (default true)
Connect to the EKS cluster using the generated config file:
export KUBECONFIG=~/.kube/eksctl/clusters/openfaas
kubectl get nodes
You will be using Helm to install OpenFaaS. For Helm to work with EKS you need version 2.9.1 or newer.
Install Helm CLI with Homebrew:
brew install kubernetes-helm
Create a service account and a cluster role binding for Tiller:
kubectl -n kube-system create sa tiller
kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller-cluster-rule \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller
Deploy Tiller on EKS:
helm init --skip-refresh --upgrade --service-account tiller
Install OpenFaaS with Helm
Create the OpenFaaS namespaces:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openfaas/faas-netes/master/namespaces.yml
Generate a random password and create an OpenFaaS credentials secret:
password=$(head -c 12 /dev/urandom | shasum | cut -d' ' -f1)
kubectl -n openfaas create secret generic basic-auth \
--from-literal=basic-auth-user=admin \
--from-literal=basic-auth-password=$password
Install OpenFaaS from the project helm repository:
helm repo add openfaas https://openfaas.github.io/faas-netes/
helm upgrade openfaas --install openfaas/openfaas \
--namespace openfaas \
--set functionNamespace=openfaas-fn \
--set serviceType=LoadBalancer \
--set basic_auth=true \
--set operator.create=true
Find the gateway address (it could take some time for the ELB to be online):
export OPENFAAS_URL=$(kubectl -n openfaas describe svc/gateway-external | grep Ingress | awk '{ print $NF }'):8080
Run echo http://$OPENFAAS_URL to get the URL for the OpenFaaS UI portal.
Install the OpenFaaS CLI and use the same credentials to login:
curl -sL https://cli.openfaas.com | sudo sh
echo $password | faas-cli login -u admin --password-stdin
The credentials are stored in a YAML file at ~/.openfaas/config.yaml.
Manage OpenFaaS functions with kubectl
Using the OpenFaaS CRD you can define functions as a Kubernetes custom resource:
apiVersion: openfaas.com/v1alpha2
kind: Function
metadata:
name: certinfo
namespace: openfaas-fn
spec:
name: certinfo
image: stefanprodan/certinfo:latest
# translates to Kubernetes metadata.labels
labels:
# if you plan to use Kubernetes HPA v2
# delete the min/max labels and
# set the factor to 0 to disable auto-scaling based on req/sec
com.openfaas.scale.min: "2"
com.openfaas.scale.max: "12"
com.openfaas.scale.factor: "4"
# translates to Kubernetes container.env
environment:
output: "verbose"
debug: "true"
# secrets are mounted as readonly files at /var/openfaas/secrets
# if you use a private registry add your image pull secret to the list
secrets:
- my-key
- my-token
# translates to Kubernetes resources.limits
limits:
cpu: "1000m"
memory: "128Mi"
# translates to Kubernetes resources.requests
requests:
cpu: "10m"
memory: "64Mi"
# translates to Kubernetes nodeSelector
constraints:
- "beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64"
Save the above resource as certinfo.yaml and use kubectl to deploy the function:
kubectl -n openfaas-fn apply -f certinfo.yaml
Since certinfo requires the my-key and my-token secrets, the Operator will not be able to create a deployment but
will keep retrying.
View the operator logs with:
kubectl -n openfaas logs deployment/gateway -c operator
controller.go:215] error syncing 'openfaas-fn/certinfo': secret "my-key" not found
Let’s create the secrets:
kubectl -n openfaas-fn create secret generic my-key --from-literal=my-key=demo-key
kubectl -n openfaas-fn create secret generic my-token --from-literal=my-token=demo-token
Once the secrets are in place the Operator will proceed with the certinfo deployment. You can get the status of the running functions with:
kubectl -n openfaas-fn get functions
NAME AGE
certinfo 4m
kubectl -n openfaas-fn get deployments
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
certinfo 1 1 1 1 1m
Test that secrets are available inside the certinfo pod at var/openfaas/secrets:
export CERT_POD=$(kubectl get pods -n openfaas-fn -l "app=certinfo" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl -n openfaas-fn exec -it $CERT_POD -- sh
~ $ cat /var/openfaas/secrets/my-key
demo-key
~ $ cat /var/openfaas/secrets/my-token
demo-token
You can delete a function with:
kubectl -n openfaas-fn delete function certinfo
Setup OpenFaaS Gateway with Let’s Encrypt TLS
When exposing OpenFaaS on the internet you should enable HTTPS to encrypt all traffic. To do that you’ll need the following tools:
- Heptio Contour as Kubernetes Ingress controller
- JetStack cert-manager as Let’s Encrypt provider
Heptio Contour is an ingress controller based on Envoy reverse proxy that supports dynamic configuration updates. Install Contour with:
kubectl apply -f https://j.hept.io/contour-deployment-rbac
Find the Contour address with:
kubectl -n heptio-contour describe svc/contour | grep Ingress | awk '{ print $NF }'
Go to your DNS provider and create a CNAME record for OpenFaaS, something like:
$ host openfaas-eks.weavedx.com
openfaas-eks.weavedx.com is an alias for a3ed4798d829511e8ae6402c29a3fb92-1221266221.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com.
a3ed4798d829511e8ae6402c29a3fb92-1221266221.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com has address 52.42.237.76
a3ed4798d829511e8ae6402c29a3fb92-1221266221.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com has address 34.209.173.53
Install cert-manager with Helm:
helm install --name cert-manager \
--namespace kube-system \
stable/cert-manager
Create a cluster issuer definition (replace EMAIL@DOMAIN.NAME with a valid email address):
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt
spec:
acme:
email: EMAIL@DOMAIN.NAME
http01: {}
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-cert
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
Save the above resource as letsencrypt-issuer.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./letsencrypt-issuer.yaml
Create an ingress definition for OpenFaaS (replace openfaas-eks.weavedx.com with your own domain name):
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "contour"
certmanager.k8s.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt"
contour.heptio.com/request-timeout: "30s"
contour.heptio.com/num-retries: "3"
contour.heptio.com/retry-on: "gateway-error"
hosts:
- host: openfaas-eks.weavedx.com
serviceName: gateway
servicePort: 8080
path: /
tls:
- secretName: openfaas-cert
hosts:
- openfaas-eks.weavedx.com
Save the above resource as ingress.yaml and upgrade the OpenFaaS release with Helm:
helm upgrade --reuse-values -f ./ingress.yaml openfaas openfaas/openfaas
In a couple of seconds cert-manager should fetch a certificate from LE:
kubectl -n kube-system logs deployment/cert-manager-cert-manager
successfully obtained certificate: cn="openfaas-eks.weavedx.com" altNames=[openfaas-eks.weavedx.com] url="https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/acme/order/37983868/14618101"
Certificate issued successfully
Verify the certificate with certinfo function:
curl -d "openfaas-eks.weavedx.com" https://openfaas-eks.weavedx.com/function/certinfo
Host 52.42.237.76
Port 443
Issuer Let's Encrypt Authority X3
CommonName openfaas-eks.weavedx.com
NotBefore 2018-07-08 09:41:15 +0000 UTC
NotAfter 2018-10-06 09:41:15 +0000 UTC
SANs [openfaas-eks.weavedx.com]
TimeRemaining 2 months from now
Conclusion
The OpenFaaS Operator offers more options for managing functions on top of Kubernetes. Besides the faas-cli and the OpenFaaS UI, you can now use kubectl, Helm charts and Weave Flux to build your CI/CD pipelines. Running OpenFaaS on EKS and Weave Cloud you get a production ready function-as-a-service platform with builtin continuous deployment, monitoring and alerting.
If you have questions about the operator please join the #kubernetes channel on
OpenFaaS Slack.
