This is a step by step guide on setting up HTTPS load balancing and basic-auth with Kubernetes Ingress for OpenFaaS Gateway on GKE.
Deploy OpenFaaS
I’m assuming you already have a GKE project with gcloud and kubectl configured to target your cluster.
Create a cluster admin user:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding "cluster-admin-$(whoami)" \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--user="$(gcloud config get-value core/account)"
Deploy OpenFaaS:
kubectl apply -f \
https://github.com/stefanprodan/openfaas-gke/releases/download/v0.1/openfaas.yaml
This will create the pods, deployments and services for the OpenFaaS gateway, faas-netesd (K8S controller), Prometheus, Alert Manager, Nats and the Queue worker.
DNS Setup
The first step in setting up the Google Cloud L7 load balancer is reserving a global public IP:
gcloud compute addresses create openfaas-ip --global
Find out what IP address you’ve been assigned:
gcloud compute addresses describe openfaas-ip --global
Use this IP to create a DNS A record for your openfaas sub domain.
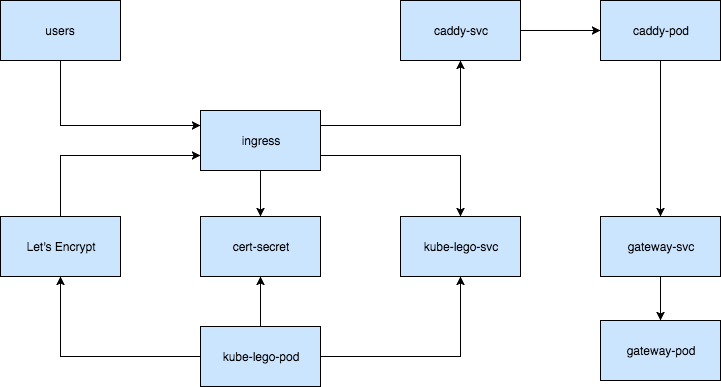
Let’s Encrypt Setup
We’ll be using kube-lego to automate the Let’s Encrypt certificate request and renewal.
Create a file named lego-cfg.yaml with the following content:
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: kube-lego
namespace: openfaas
data:
lego.email: "contact@example.com"
lego.url: "https://acme-v01.api.letsencrypt.org/directory"
Replace contact@example.com with a valid email address, Let’s Encrypt will contact you
if there is a problem with your certificate.
Assuming you’re running the OpenFaaS Gateway in the openfaas namespace, let’s deploy the config with kubectl:
kubectl apply -f ./lego-cfg.yaml
Next we need to create a service account and a cluster role binding for kube-lego to be able to operate:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: kube-lego
namespace: openfaas
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: kube-lego
rules:
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- list
- get
- create
- update
- delete
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- endpoints
- services
- secrets
verbs:
- get
- create
- update
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: kube-lego
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: kube-lego
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: kube-lego
namespace: openfaas
Save the above YAML as lego-rbac.yaml and apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./lego-rbac.yaml
Now let’s create the kube-lego deployment file:
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kube-lego
namespace: openfaas
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: kube-lego
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: kube-lego
spec:
serviceAccountName: kube-lego
containers:
- name: kube-lego
image: jetstack/kube-lego:0.1.5
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: LEGO_LOG_LEVEL
value: debug
- name: LEGO_EMAIL
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: kube-lego
key: lego.email
- name: LEGO_URL
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: kube-lego
key: lego.url
- name: LEGO_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: LEGO_POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 1
Save the above YAML as lego-dep.yaml and apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./lego-dep.yaml
Reverse Proxy Setup
We’ll be using Caddy as a reverse proxy, health check and basic-auth provider for the OpenFaaS Gateway.
First create the Caddy config file:
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: caddy-tls-config
namespace: openfaas
labels:
app: caddy-tls
data:
Caddyfile: |
:80 {
status 200 /healthz
basicauth /system {$ADMIN_USER} {$ADMIN_PASSWORD}
basicauth /ui {$ADMIN_USER} {$ADMIN_PASSWORD}
proxy / gateway:8080 {
transparent
}
errors stderr
tls off
}
Create the basic-auth secret and apply caddy-cfg.yaml:
kubectl -n openfaas create secret generic basic-auth-tls \
--from-literal=user=admin \
--from-literal=password=admin
kubectl apply -f ./caddy-cfg.yaml
Next let’s create the Caddy deployment with a readiness probe pointing to the /healthz endpoint.
The readiness probe will be used by the Ingress controller health checks.
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: caddy-tls
namespace: openfaas
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: caddy-tls
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: caddy-tls
spec:
containers:
- name: caddy-tls
image: stefanprodan/caddy:0.10.10
imagePullPolicy: Always
command: ["caddy", "-agree", "--conf", "/Caddyfile"]
env:
- name: ADMIN_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: basic-auth-tls
key: user
- name: ADMIN_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: basic-auth-tls
key: password
ports:
- containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 1
resources:
limits:
memory: 128Mi
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /Caddyfile
name: caddy-config
subPath: Caddyfile
volumes:
- name: caddy-config
configMap:
name: caddy-tls-config
items:
- key: Caddyfile
path: Caddyfile
mode: 0644
Save the above YAML as caddy-dep.yaml and apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./lego-dep.yaml
Next we need to create a NodePort Service to serve as backend for the GKE Ingress controller:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: caddy-tls-svc
namespace: openfaas
annotations:
prometheus.io.scrape: 'false'
labels:
app: caddy-tls
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
name: web
nodePort: 30049
selector:
app: caddy-tls
Save the above YAML as caddy-svc.yaml and apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./lego-svc.yaml
Ingress Setup
Now it’s time to create the Ingress definition using the static IP and the Caddy service as backend:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: openfaas-ingress
namespace: openfaas
annotations:
kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "gce"
kubernetes.io/ingress.global-static-ip-name: openfaas-ip
prometheus.io.scrape: 'false'
labels:
app: caddy-tls
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- openfaas.example.com
secretName: openfaas-tls
rules:
- host: openfaas.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /*
backend:
serviceName: caddy-tls-svc
servicePort: 80
Replace openfaas.example.com with you’re own domain, save the YAML as ingress-tls.yaml and apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./ingress-tls.yaml
It will take at least 10 minutes for the GCP load balancer to become healthy. You can check the Ingress status with:
kubectl -n openfaas describe ingress openfaas-ingress
Once the Ingress is up, kube-lego will attach a new backend to the load balancer and will request a certificate.
Kube-lego will create a secret named openfaas-tls that will contain the Let’s Encrypt certificate, from there
the GCP load balancer will load the certificate and you will be able to access the OpenFaaS
at https://openfaas.example.com.
If you have any suggestion on improving this guide please submit an issue or PR on GitHub at stefanprodan/openfaas-gke. Contributions are more than welcome!
